January brings renewed motivation for patients, but clinical experience shows that topical regimens often fail due to complexity, irritation, or poor follow-through, not lack of intent. The new year is an ideal time for clinicians to reset expectations, simplify routines, and reinforce skin barrier support and scar care protocols that patients can realistically maintain.
Why adherence breaks down
Recent medical literature consistently shows lower adherence with topical regimens compared to systemic therapies. The most common barriers include unclear instructions, time burden, cosmetic dissatisfaction, and uncertainty about duration of use. Simplifying regimens and reinforcing education meaningfully improves follow-through and outcomes.
Practical Strategies Clinicians Can Implement Now
-
Start with barrier support
Daily moisturization remains foundational for inflamed, compromised, or treatment-stressed skin. Selecting a gentle, cosmetically acceptable moisturizer improves consistency and supports recovery. Products such as Skin Recovery Cream can be positioned as part of a daily, non-negotiable routine rather than an optional add-on. -
Match scar therapy to patient behavior
Silicone-based scar management remains a widely supported option for hypertrophic and postsurgical scars, but outcomes correlate strongly with compliance.
-
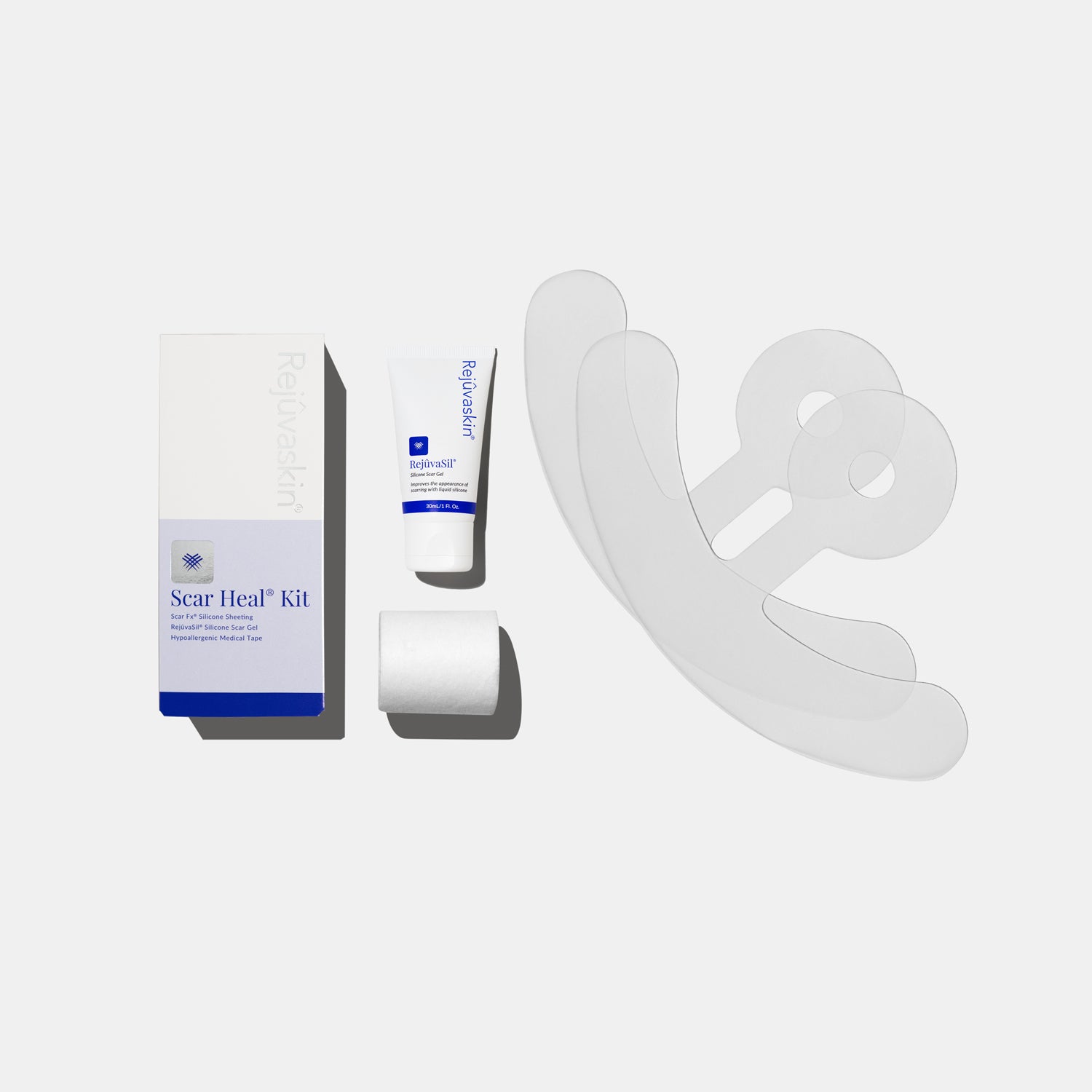
Silicone sheeting may be ideal when patients can tolerate extended wear (e.g., Scar Fx Silicone Sheeting).
-
Silicone gels or creams may improve adherence in mobile areas or for patients sensitive to occlusion (e.g., RejuvaSil Silicone Scar Gel or Scar Esthetique Silicone Scar Cream).
-
Reduce friction with systems, not instructions
Bundled approaches, such as Scar Heal Kits, help standardize care, reduce decision fatigue, and improve consistency by giving patients a clear start-to-finish routine. -
Set expectations early and revisit them often
Patients benefit from knowing what is normal, how long results take, and what to do if irritation occurs. Brief follow-ups or written protocols significantly improve adherence over time.
The Clinical Takeaway
In the new year, better outcomes come from simpler plans, barrier-first skin support, and scar therapies that align with real-world patient behavior. When clinicians focus on tolerability, clarity, and consistency, patients are more likely to stay engaged and see meaningful improvement.
References
-
Patient adherence in dermatology: A practical review of barriers and solutions. Dermatology Review, 2024.
-
Comparison of adherence between topical and systemic dermatologic therapies using MMAS-8. Journal of Dermatological Treatment, 2025.
-
Skin barrier dysfunction and repair strategies in atopic dermatitis. Clinical Dermatology Reviews, 2024.
-
Ceramide-based and barrier-support moisturizers in inflammatory skin disease: A randomized clinical study. Journal of Drugs in Dermatology, 2024.
-
Practical recommendations for the prevention and management of radiation-induced dermatitis. Supportive Care in Cancer, 2025.
-
Skin management guidelines for patients undergoing radiation therapy. MD Anderson Cancer Center, 2024.
-
Compliance with silicone gel and silicone gel sheeting and its association with scar outcomes: A randomized clinical trial. Burns & Trauma, 2024.
-
Efficacy of silicone gel sheeting for hypertrophic burn scars: A within-patient randomized controlled trial. Burns, 2025.
-
Clinical practice guideline for pediatric hypertrophic scar and keloid management. 2025.