Breast surgery, whether for medical or cosmetic reasons, is a significant event. While the surgery can improve your physical comfort and confidence, a common concern for many patients is scarring. Fortunately, with the right care and scientifically-backed approaches, it is possible to minimize scar formation and improve skin healing.
In this article, I’ll guide you through evidence-based strategies for caring for your skin post-surgery and reducing scars. These tips, supported by clinical research, will help ensure a smoother recovery.
What Happens to Your Skin After Surgery?
When your skin is incised during surgery, it goes through a healing process that involves the production of collagen. Collagen is essential for wound healing, but it can sometimes form in irregular patterns, leading to scar formation. Scars can vary in appearance depending on factors like genetics, wound care, and post-surgical treatments. However, there are scientifically proven ways to support the skin's healing and minimize scar formation.
Top 5 Tips for Preventing and Minimizing Scars After Breast Surgery
1. Follow Your Surgeon’s Instructions
Post-operative care instructions provided by your surgeon are crucial for minimizing scars. According to a 2014 study, proper wound care, including keeping the area clean and dry, significantly reduces the risk of infection, which can exacerbate scar formation. It's essential to avoid stretching the skin at the incision site too soon, as this can disrupt the healing process and result in more noticeable scars (Gold et al., 2014).
2. Use Silicone-Based Products
Silicone has been extensively researched for its role in reducing scar formation. Multiple studies support the effectiveness of silicone in improving scar texture and color by maintaining moisture in the scarred area and creating a protective barrier that shields the healing tissue from bacteria and irritants.
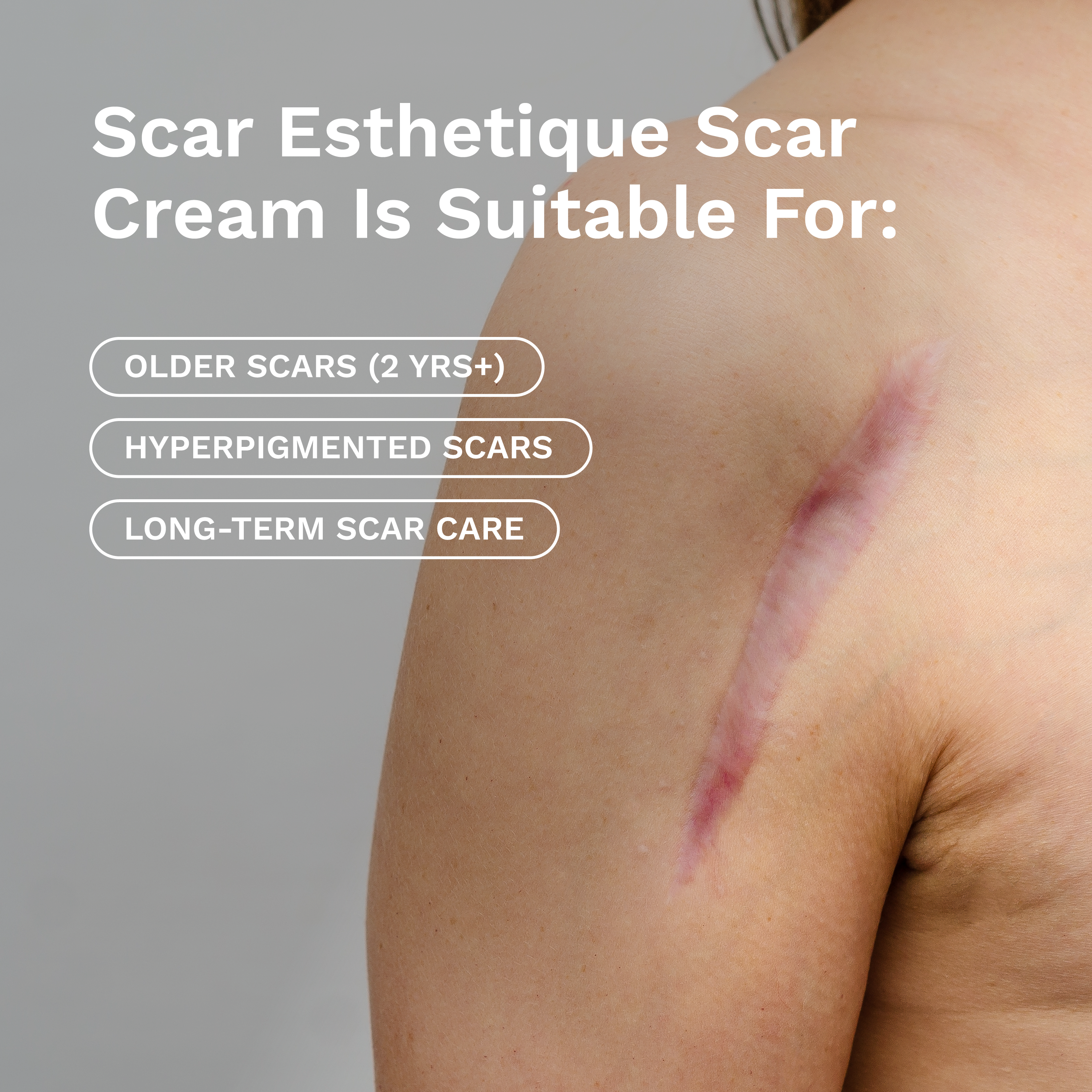
A systematic review in the Advances in Skin & Wound Care journal highlighted the effectiveness of silicone gel sheets in the management of hypertrophic scars and keloids. Patients using silicone gel sheeting experienced improvements in scar thickness, redness, and texture (Carter et al., 2019).
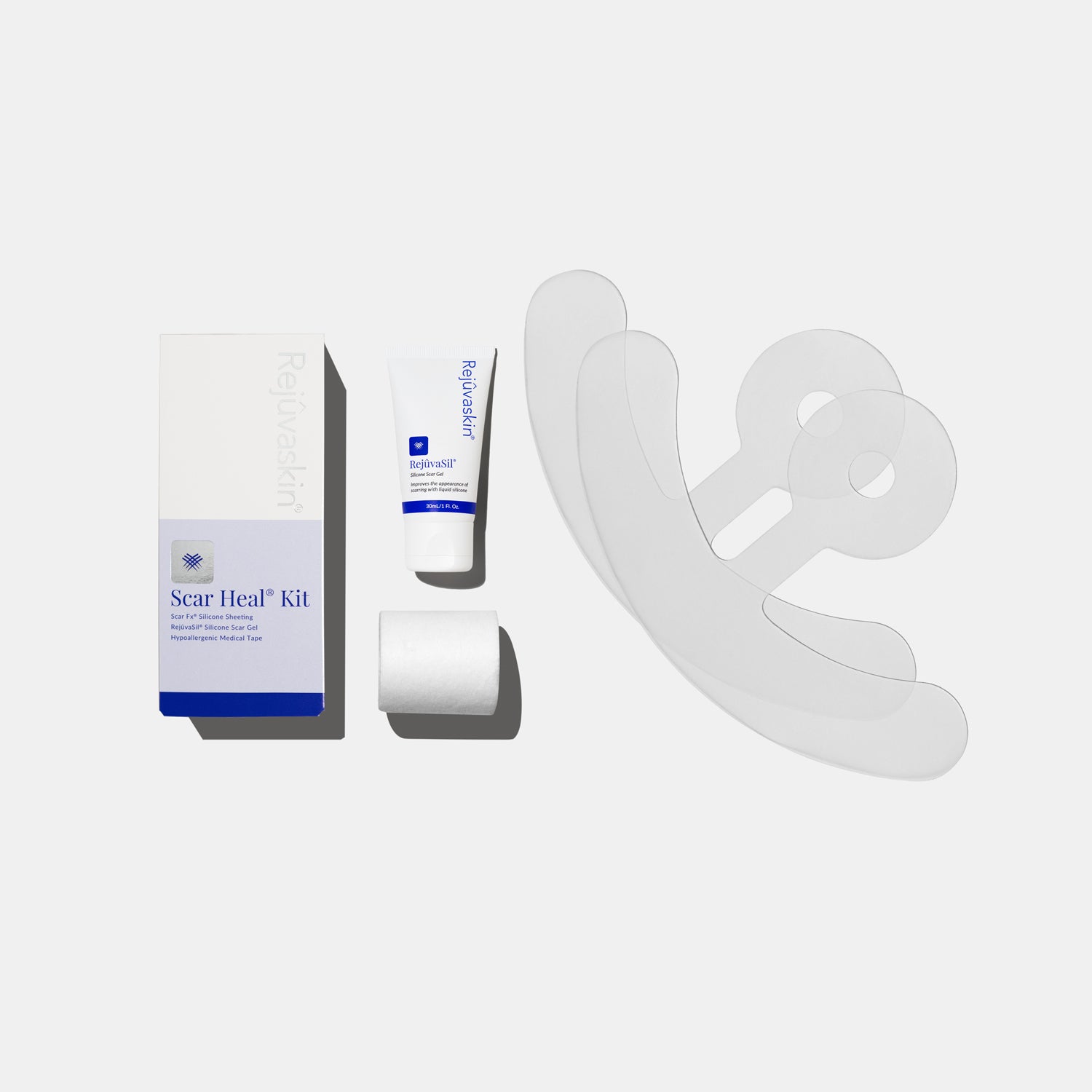
Products such as Rejuvaskin Scar Heal Kit, Rejuvaskin Silicone Scar Cream, and RejuvaSil® Silicone Scar Gel are commonly recommended by dermatologists and plastic surgeons. These products help regulate collagen production, which can prevent raised or thick scars from forming.
3. Gently Massage the Area
Once your surgical wound has fully healed (usually after a few weeks), gentle massage of the scar area can be beneficial. A study published in the American Journal of Clinical Dermatology found that massaging the scar area helps promote collagen remodeling, leading to smoother and less raised scars (Alster & Tanzi, 2003). Massaging also improves blood flow to the tissue, which supports overall healing.
To enhance the benefits, use RejuvaSil® Silicone Scar Gel while massaging the scarred area. This will provide additional hydration and protection to the healing skin.
4. Protect Your Scars from Sun Exposure
Exposure to ultraviolet (UV) light can worsen the appearance of scars by causing hyperpigmentation (darkening of the scar). The skin in a scar is especially sensitive to sun damage. A study from the Journal of Plastic, Reconstructive & Aesthetic Surgery recommended using sunscreen with an SPF of at least 30 on scars to prevent discoloration and further damage. Applying sunscreen once your surgeon gives the green light for topical treatments is an essential part of scar management.
Additionally, products like Scar Fx® Silicone Sheeting not only help flatten the scar but also provide a physical barrier to protect the healing skin from UV rays.
5. Support Healing from the Inside
A balanced diet rich in vitamins and nutrients can promote optimal skin healing. Nutrients like vitamins A, C, and E, along with zinc, play a critical role in collagen formation and tissue repair. Clinical studies have shown that deficiencies in these vitamins can delay wound healing, while adequate intake supports faster and more effective recovery (Guo & DiPietro, 2010).
Additionally, avoiding smoking is essential. Smoking reduces blood flow to healing tissues, which can result in delayed wound healing and poor scar outcomes (Guo & DiPietro, 2010).
Which Silicone-Based Product is Right for You?
If you're looking for silicone products to improve scar healing, here are some recommendations based on clinical evidence:
- Silicone sheeting: Best for larger scars, such as those from breast surgery, as it provides continuous pressure and hydration, reducing the risk of hypertrophic scars. Find out which sheet is best for your scar!
- Silicone gel: Ideal for smaller or more mobile areas, providing a breathable barrier and protecting scars from moisture loss and environmental damage.
- Silicone creams: These can be beneficial for individuals with sensitive skin, offering hydration while maintaining flexibility in the healing skin.
Final Thoughts
Minimizing scarring after breast surgery is possible with a combination of proper wound care, the use of scientifically supported silicone products, and healthy lifestyle habits. Following your surgeon’s advice and staying consistent with scar treatment strategies will help you achieve the best results.
Remember, healing is a gradual process, and patience is key. With time and the right approach, your scars will become less noticeable, allowing you to focus on feeling confident and comfortable in your skin.
References:
- Gold, M. H., McGuire, M., Mustoe, T. A., Pusic, A., & Sachdev, M. (2014). Updated international clinical recommendations on scar management: Part 2—Algorithmic approach for scar prevention and treatment following surgery. Dermatologic Surgery, 40(8), 825-831.
- Alster, T. S., & Tanzi, E. L. (2003). Hypertrophic scars and keloids: Etiology and management. American Journal of Clinical Dermatology, 4(4), 235-243.
- Carter, M. J., Fife, C. E., & Walker, D. (2019). Silicone gel sheeting for the management of hypertrophic scars and keloids. Advances in Skin & Wound Care, 32(12), 568-574.
- Guo, S., & DiPietro, L. A. (2010). Factors affecting wound healing. Journal of Dental Research, 89(3), 219-229.



















Leave a comment