At Rejuvaskin, we understand that skin health isn't just about what you apply topically—it's also about what's happening inside your body. Emerging research highlights a fascinating link between gut health and skin conditions like eczema.This connection, known as the "gut-skin axis," suggests that maintaining a healthy digestive system can play a crucial role in managing and preventing eczema flare-ups.
Understanding the Gut-Skin Axis
The gut-skin axis refers to the complex communication network between your gastrointestinal tract and your skin. This relationship is mediated by the immune system, hormones, and the nervous system. An imbalance in the gut microbiome—often termed "dysbiosis"—can lead to systemic inflammation, which may manifest as skin conditions, including eczema.
Research indicates that individuals with eczema often exhibit reduced diversity in their gut microbiota compared to those without the condition. This decreased diversity can compromise the gut barrier, allowing toxins and pathogens to enter the bloodstream, potentially triggering inflammatory skin responses. PMC
Scientific Insights: Gut Health and Eczema
-
Infant Gut Microbiome and Eczema: Studies have found that infants with less diverse gut microbiota are more susceptible to developing eczema. PMC
-
Leaky Gut Syndrome: A compromised gut lining can allow harmful substances to enter the bloodstream, leading to systemic inflammation and skin issues like eczema. National Eczema Association
-
Probiotics and Skin Health: Certain probiotic strains, such as Lactobacillus paracasei, have been shown to improve skin barrier function and reduce sensitivity, potentially benefiting those with eczema. PMC
Supporting Gut Health for Better Skin
While more research is needed, several strategies may help maintain a healthy gut microbiome, potentially alleviating eczema symptoms:
-
Dietary Fiber: Consuming a diet rich in fiber can promote a diverse and healthy gut microbiome.
-
Fermented Foods: Incorporating fermented foods like yogurt, kefir, and sauerkraut can introduce beneficial bacteria to the gut.
-
Probiotics and Prebiotics: Supplementing with probiotics and prebiotics may help restore gut microbial balance, though individual responses can vary. J Integrative Derm
-
Stress Management: Chronic stress can negatively impact gut health; therefore, stress-reducing practices may benefit both gut and skin health.
Topical Support: Strengthening the Skin Barrier
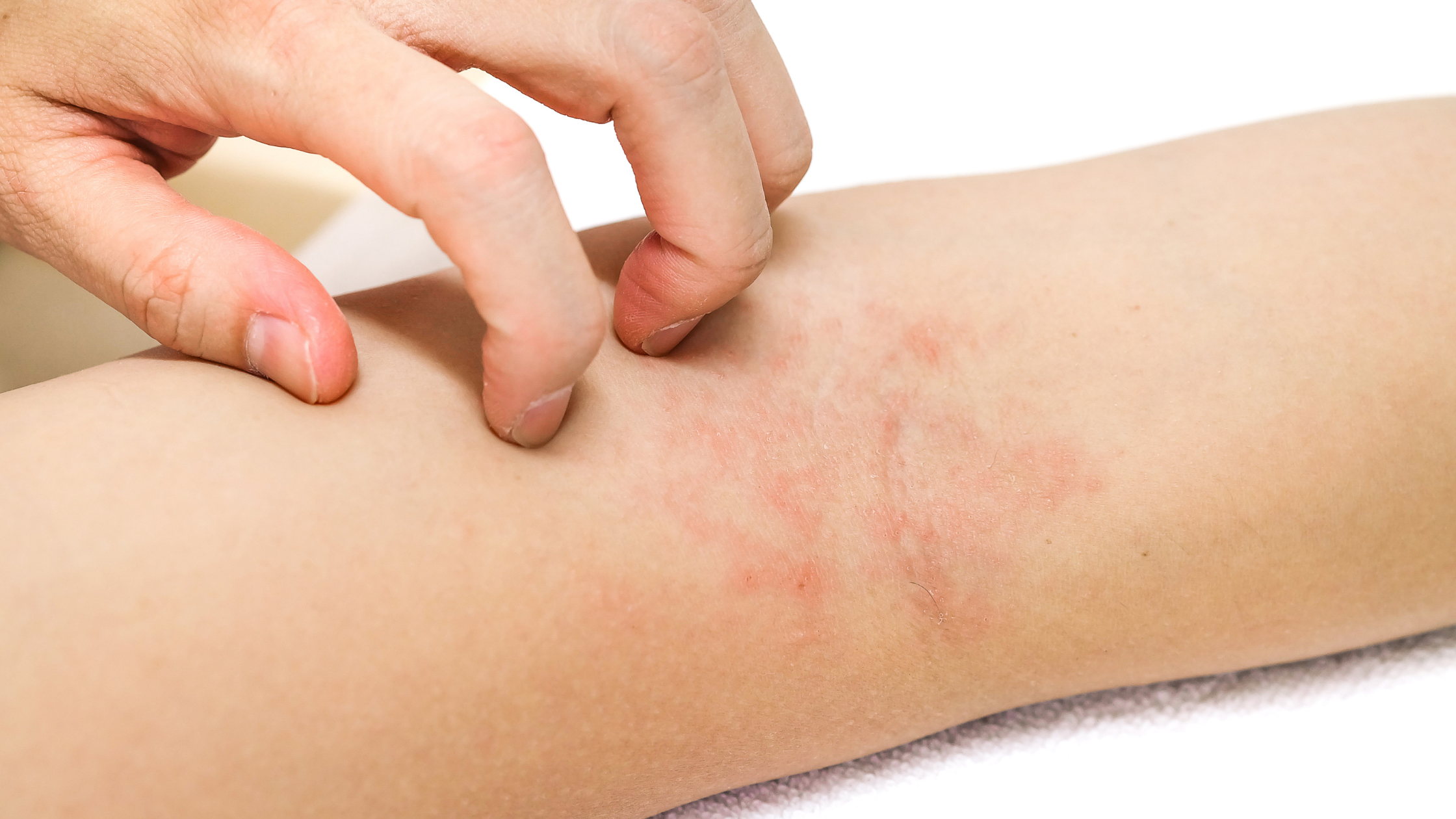
While addressing gut health is important, supporting the skin externally remains crucial. Using products that reinforce the skin's barrier can help protect against environmental irritants and moisture loss, common issues in eczema.
Rejuvaskin's Skin Recovery Cream is formulated to hydrate and soothe irritated skin, making it an excellent addition to your skincare routine. Its non-irritating, hydrating properties can help maintain skin barrier integrity, complementing internal health strategies.
The interplay between gut health and eczema underscores the importance of a holistic approach to managing skin conditions. By nurturing the gut microbiome through diet, lifestyle, and possibly supplementation, individuals may find relief from eczema symptoms. Coupled with topical treatments that strengthen the skin barrier, this comprehensive strategy offers a promising path for those affected by eczema.
Works Cited
-
National Eczema Association. (n.d.). Leaky Gut and Atopic Dermatitis. Retrieved from link
-
PubMed Central. (n.d.). Microbiome in the Gut-Skin Axis in Atopic Dermatitis. Retrieved from link
-
Journal of Integrative Dermatology. (n.d.). Postbiotics and Atopic Dermatitis: Aiming to Modulate the Gut-Skin Axis. link


















Leave a comment