Scars may seem like a simple part of healing—but behind every scar is an extraordinary biological process. Whether you're recovering from surgery, a C-section, acne, or a burn, understanding the science of how your skin repairs itself can help you make smarter decisions about your care.
At Rejuvaskin, we believe that healing isn’t just about covering up—it's about optimizing the process. Let’s break down the four stages of skin repair, explore why scars form, and show how modern scar treatments like silicone can support healthier, more confident skin recovery.
The 4 Stages of Wound Healing
1. Hemostasis
The first response to injury is to stop the bleeding. Platelets form a clot and release growth factors to trigger tissue repair.
2. Inflammation
Immune cells flood the area to remove bacteria and damaged tissue. Inflammation is essential—but prolonged inflammation can delay healing and worsen scarring (Potter et al., 2019).
3. Proliferation
New tissue begins to form. Fibroblasts produce collagen and extracellular matrix, while epithelial cells migrate to close the wound.
4. Remodeling (Maturation)
Over weeks to months, collagen is reorganized to strengthen the skin. But in adults, this often results in scar tissue, which lacks the flexibility and features of healthy skin (Nguyen et al., 2023).
Why Do Scars Form?
Scarring is the body’s way of sealing a wound quickly to protect against infection. But fast healing isn’t always perfect. The new tissue formed during repair:
-
Is collagen-rich, but often disorganized
-
Lacks structures like sweat glands and hair follicles
-
May appear raised, discolored, or tight
In some cases, this process produces hypertrophic or keloid scars, which are harder, thicker, and more visible.
How Silicone Supports Better Healing
Medical-grade silicone gel and sheets are now considered the first-line, non-invasive treatment for scars by dermatologists and surgeons worldwide. Here's why:
-
Hydration + Occlusion: Silicone keeps the wound site moist and protected, which promotes remodeling and flattens scars.
-
Collagen Regulation: Silicone helps normalize collagen production, reducing the risk of thick, raised scars (Liu, 2009).
-
Comfort and Flexibility: Silicone sheets are easy to wear, reusable, and suitable for all skin tones and types.
In a recent clinical comparison, silicone outperformed standard wound dressings in reducing scar elevation, redness, and discomfort after surgery (Moore & Silbernagel, 2010).
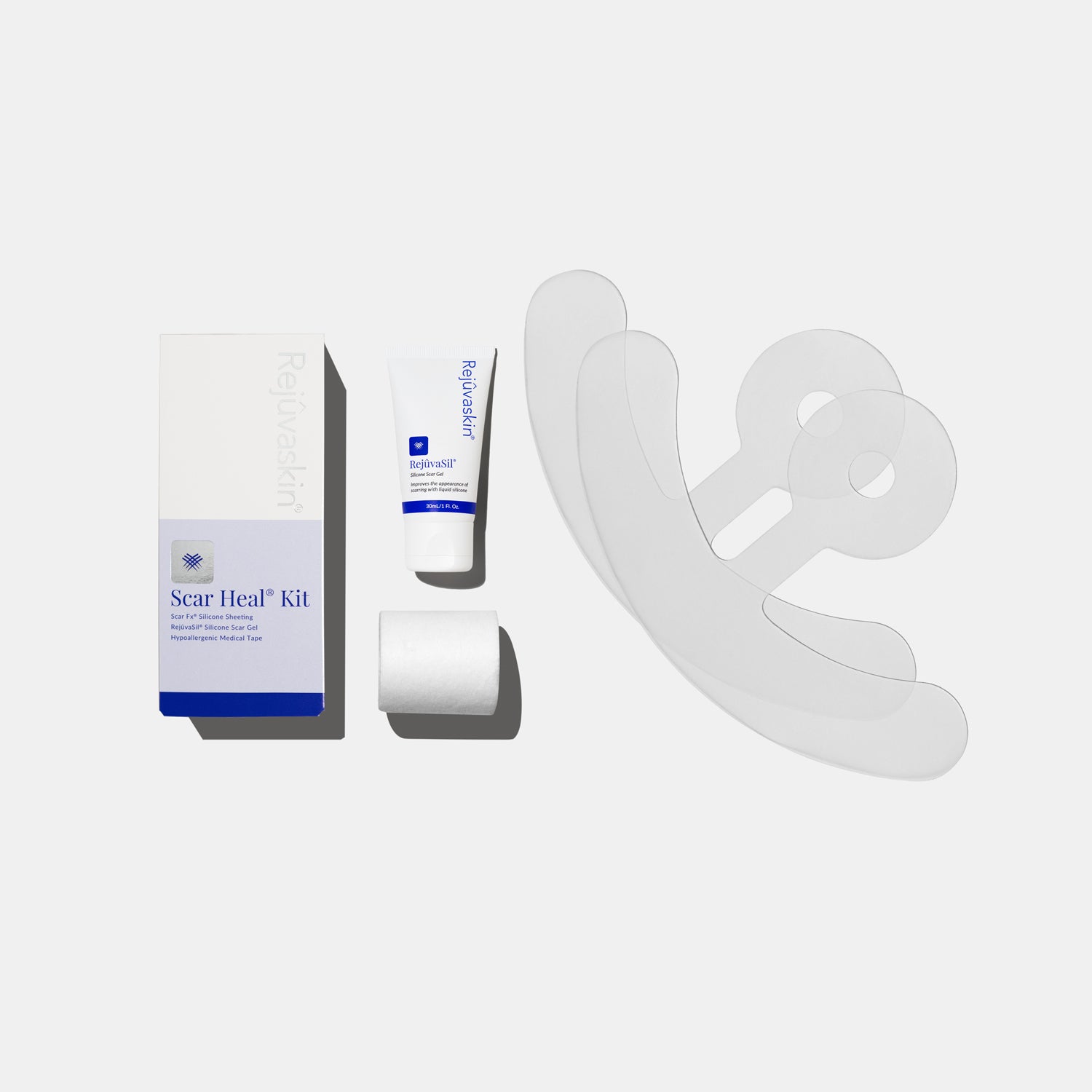
Rejuvaskin’s Scar Fx® Silicone Sheeting and Advanced Scar Gel are trusted by dermatologists, plastic surgeons, and patients worldwide. Here’s what makes them different:
-
100% medical-grade silicone
-
Gentle on sensitive skin (ideal for surgical and pediatric scars)
-
Reusable up to 30-45 days
-
Clinically backed ingredients to support smoother, flatter scars
-
Designed for all scar types: surgical, traumatic, burn, acne, and more
When used consistently after wound closure, Rejuvaskin products support skin’s natural healing and help reduce visible signs of scarring.
Tips for Optimizing Healing and Minimizing Scars
-
Start early: Once the wound is fully closed, begin using silicone products.
-
Apply consistently: Wear scar sheets for 12–24 hours/day for at least 8 weeks.
-
Combine with barrier-repair skincare: Rejuvaskin's Skin Recovery Cream supports hydration, calms irritation, and improves elasticity.
Your body is built to heal—but science helps it heal better. By understanding the stages of wound healing and the role of modern treatments like silicone, you can give your skin the support it needs for smoother, more confident recovery.
Ready to take control of your healing journey? Explore Rejuvaskin’s clinically backed scar solutions and let your skin’s recovery begin.
Works Cited
-
Liu, L. (2009). The mechanism of silicone in scar treatment.
-
Moore, K. A., & Silbernagel, B. (2010). Postoperative scar formation with silicone sheeting. The Journal of the American College of Certified Wound Specialists.
-
Potter, D. A., Veitch, D., & Johnston, G. (2019). Scarring and wound healing. British Journal of Hospital Medicine.
-
Nguyen, A., Huynh, C., Goh, A., et al. (2023). Management of postoperative scars with silicone gel-based products.
-
Onselen, J. V. (2018). Scars: impact and management. British Journal of Nursing.






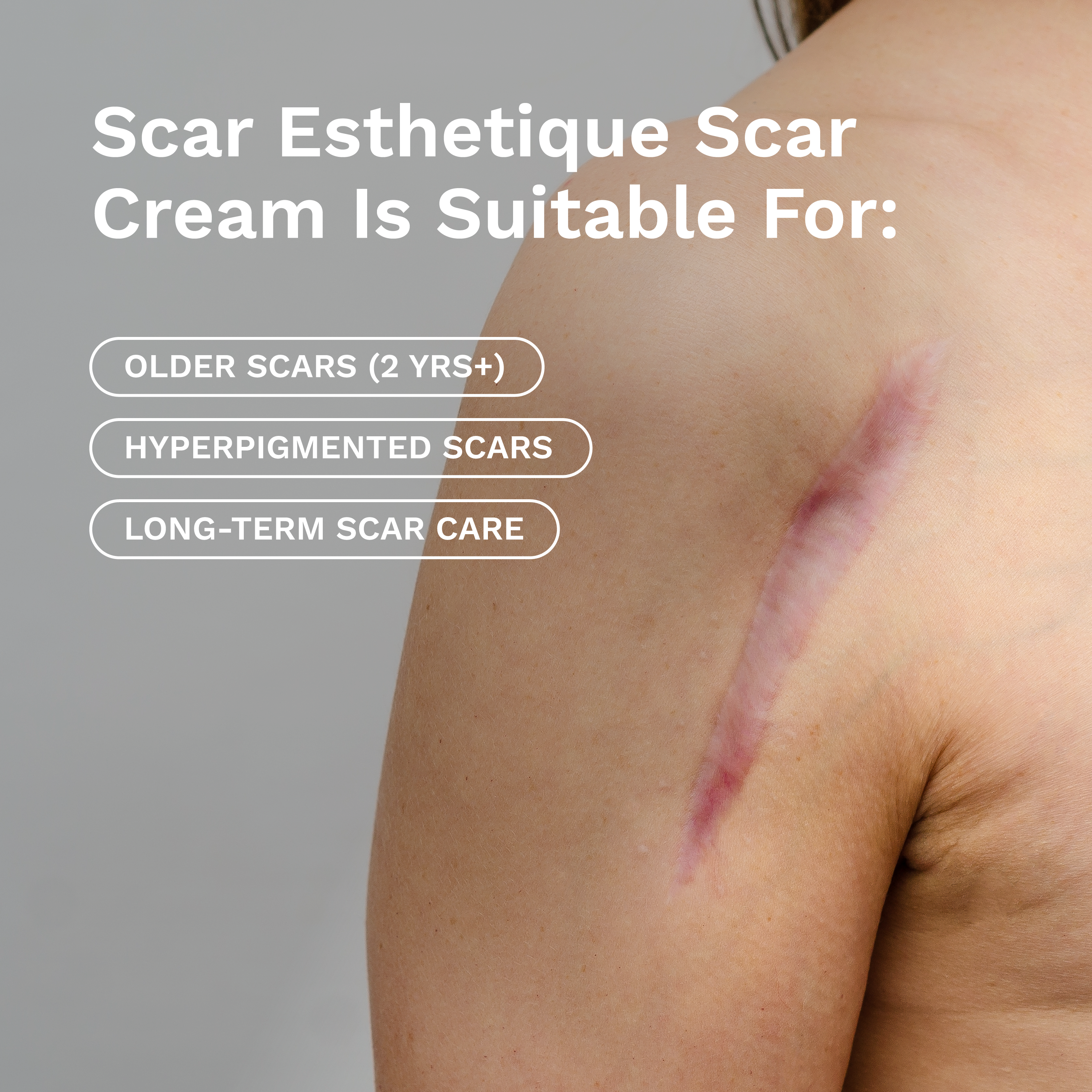













Leave a comment