While sunscreen is unable to erase existing scars, it has been empirically established as a valuable preventive measure when consistently applied to newly formed scar tissue. This proactive strategy not only curtails the worsening of scar pigmentation but also ensures protection against ultraviolet (UV) radiation, ultimately reducing scar visibility and reinforcing the resilience of delicate skin.
Creating The Right Healing Environment
In the initial postoperative phase, it's essential to maintain an ideal environment for wound healing to achieve the best possible results. Infection prevention and control are paramount in this process. This begins by creating a moisture-rich setting for scar formation.
A daily application of antibiotic ointments, like bacitracin, offers both antimicrobial benefits and the added advantage of enhancing scar outcomes through accelerated epithelialization, owing to the moisture they provide. The debate continues regarding whether the antibacterial properties of these topical agents significantly impact scar results or if the improvement is primarily due to the moisture they offer.
Typically, the application of a triple antibiotic ointment commences immediately after wound closure during the surgery and persists for one to three weeks postoperatively. One potential drawback is that some patients may develop contact dermatitis, which is not observed with petroleum jelly ointments. To mitigate the risk of allergic reactions, some physicians prefer to employ antibiotic ointment for the first week due to its antimicrobial effects, subsequently transitioning to a petroleum jelly ointment for the following one to two weeks. This approach balances the dual goals of infection prevention and scar enhancement.
Following the initial 2- to 3-week phase of scar healing, where keeping the wound adequately moisturized is key for improving epithelialization, patients may start experiencing a notable reduction in incisional discomfort. After the wound has fully healed and the scar has developed, patients may consider incorporating topical treatments into their scar care routine. These options encompass products such as Scar Fx Silicone Sheeting, RejûvaSil Silicone Scar Gel, or our comprehensive Scar Heal Kits featuring both silicone sheeting and silicone gel components. This proactive approach to scar management can significantly contribute to optimal healing outcomes.
When It’s Time For Sun Protection
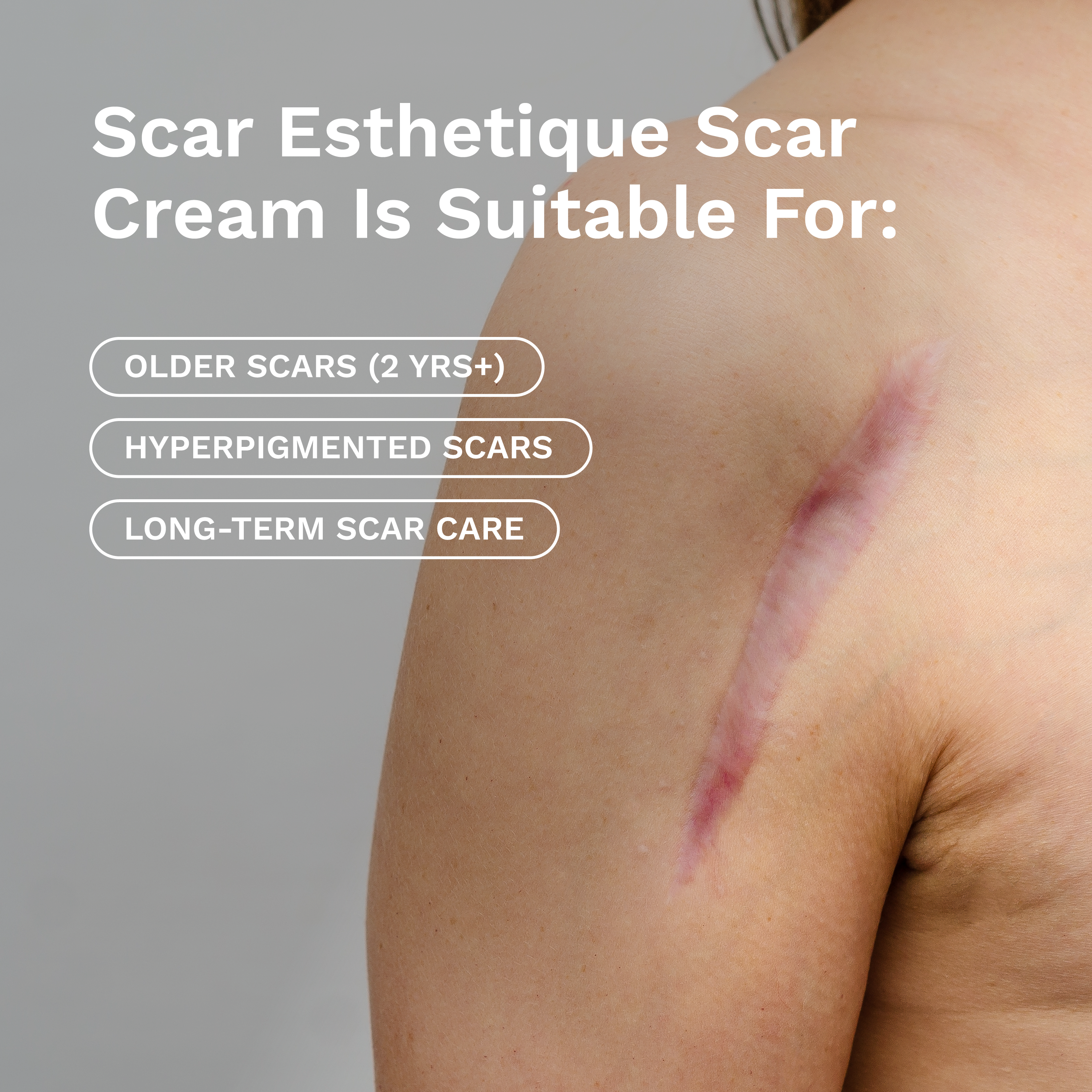
At this juncture, it is crucial to inform patients about the importance of sun protection, particularly as they resume their normal activities. Newly formed scars, especially those less than 18 months old, are highly susceptible to the adverse effects of sunlight, resulting in hyperpigmentation and structural changes in the collagen matrix, leading to thicker and discolored scars. To mitigate these effects, it is advisable to limit sun exposure to the scar by employing protective clothing or dressing. Furthermore, it is recommended that patients consistently use sunscreen with a minimum SPF of 30 during the subsequent 12 to 18 months post-surgery, ensuring protection against harmful ultraviolet radiation and its application whenever exposed to sunlight.
Beyond its primary role in reducing the risk of skin malignancies, sunscreen also contributes to minimizing scar hyperpigmentation by inhibiting melanogenesis, a process triggered by ultraviolet exposure.
-
References
Commander, S. J., Chamata, E., Cox, J., Dickey, R. M., & Lee, E. I. (2016). Update on Postsurgical Scar Management. Seminars in plastic surgery, 30(3), 122–128. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-0036-1584824