Once considered a procedure mainly for individuals in their 50s or 60s with age-related lid changes or vision obstruction, blepharoplasty (eyelid lift) is now increasingly sought by younger adults, especially women in their 30s. The shift reflects changes in cosmetic expectations, early signs of aging, hereditary traits, and broader acceptance of aesthetic surgery among younger generations.
Traditionally, blepharoplasty was performed to correct sagging from age-related tissue laxity and muscle weakening. It involves precise removal or repositioning of excess skin, muscle, and sometimes fat from the upper or lower eyelids to create a smoother, more youthful contour. This cosmetic and functional restoration has long been validated in clinical surgical literature as both safe and effective with proper patient selection and technique. (Oestreicher et al., 2012)
Emerging clinical reports increasingly document that blepharoplasty is no longer just a procedure of later life. Younger patients are turning to eyelid surgery to address persistent puffiness, stubborn upper lid skin, or disproportionate fat pads that are hereditary rather than age-induced. Although comprehensive demographic data in peer-reviewed journals on age-specific trends is still limited, clinical reviews confirm that surgical interest is mounting as part of broader aesthetic goals. (Naik et al., 2009)
Why Younger Women Are Choosing Blepharoplasty
Younger patients — including those in their 30s — cite several reasons for seeking eyelid lifts:
1. Heredity and Early Structural Concerns
Some individuals have prominent upper lid skin or under-eye fat pads that are present from a young adult age. These features can create a perpetually tired or puffy appearance that can’t be corrected with non-surgical measures alone.
2. Aesthetic Trends and Facial Balance
Subtle changes around the eyes are often targeted to enhance overall facial balance. Even minor adjustments — such as removing excess skin or refining lid contour — can produce a refreshed look, which younger adults increasingly value. Although randomized controlled trials on age trends are limited, clinical evidence supports the procedure’s ability to improve periocular aesthetics when appropriately indicated. (Oestreicher et al., 2012)
3. Functional Benefits
In some cases, excess upper lids can encroach on vision. Blepharoplasty remains a functional surgery for clinical vision impairment due to redundant tissue, and this indication does not strictly depend on age.
4. Minimally Invasive Expectations
Advances in surgical techniques, including skin-preserving approaches, have reduced downtime and made recovery more manageable. Lower complication rates — reported as generally mild and transient in the scientific literature — also contribute to patient confidence.
What the Science Says About Blepharoplasty
Peer-reviewed surgical overviews confirm that blepharoplasty is an established plastic surgical procedure with a well-characterized risk profile. Common complications can include swelling, bruising, and temporary lid asymmetries, but serious adverse outcomes are rare when performed by trained oculoplastic or plastic surgeons. These findings are based on case series and clinical management literature rather than experimental trials, given the nature of surgical research. (Naik et al., 2009)
Eyelid incisions are typically placed within natural creases so that scarring is minimal and often clinically inconspicuous. However, all surgical wounds heal through a series of biological stages, and post-operative care can influence scar quality and patient satisfaction.
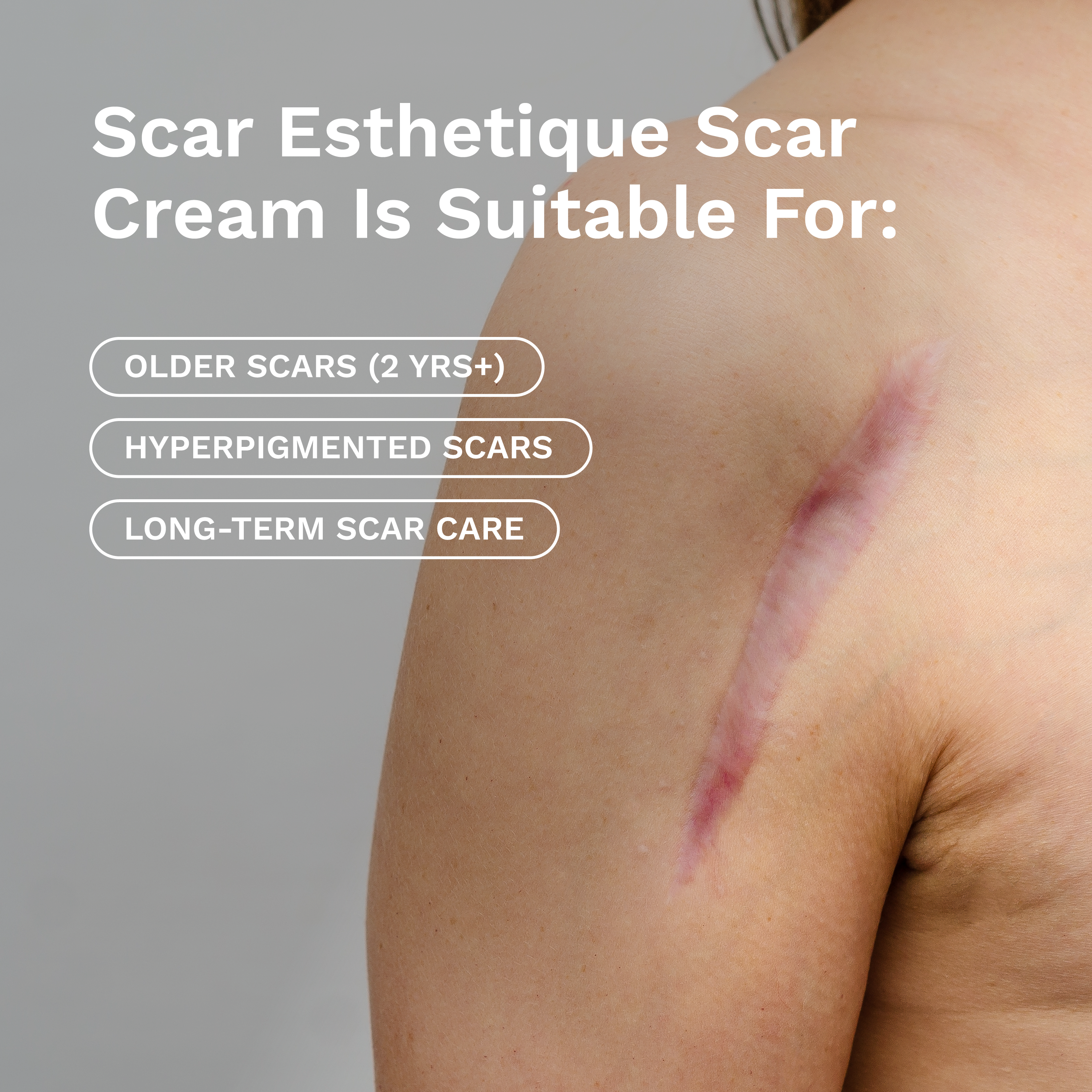
Scar Formation and Management After Eyelid Surgery
Scar tissue results from the body’s normal wound healing process, during which collagen is deposited to repair the cut tissue. While most surgical scars gradually fade, the appearance of scars can vary based on individual biology, tension on the wound, and the care taken during healing.
Extensive research supports silicone-based therapies — including silicone gels — as a first-line, evidence-based approach for scar management after closed and healed surgical wounds. Clinical trials and systematic reviews document that topical silicone gel can improve scar characteristics such as thickness, color, and texture compared with no treatment or placebo at follow-ups of 6 months or longer. (Wang et al., 2020)
Silicone’s mechanism is thought to involve semi-occlusion of the scar surface, which helps maintain hydration, modulate fibroblast activity, and support scar maturation processes. (Mechanistic analyses and clinical summaries support this effect, though precise pathways remain under study.) (Tandara & Mustoe, 2008)
Additional clinical studies and comparative analyses indicate that topical silicone gel performs similarly to silicone gel sheets, with both formulations offering preventive and therapeutic benefits in surgical scar outcomes when applied consistently after wound closure. (Kim et al., 2014)
Supporting Post-Blepharoplasty Healing With Rejuvaskin
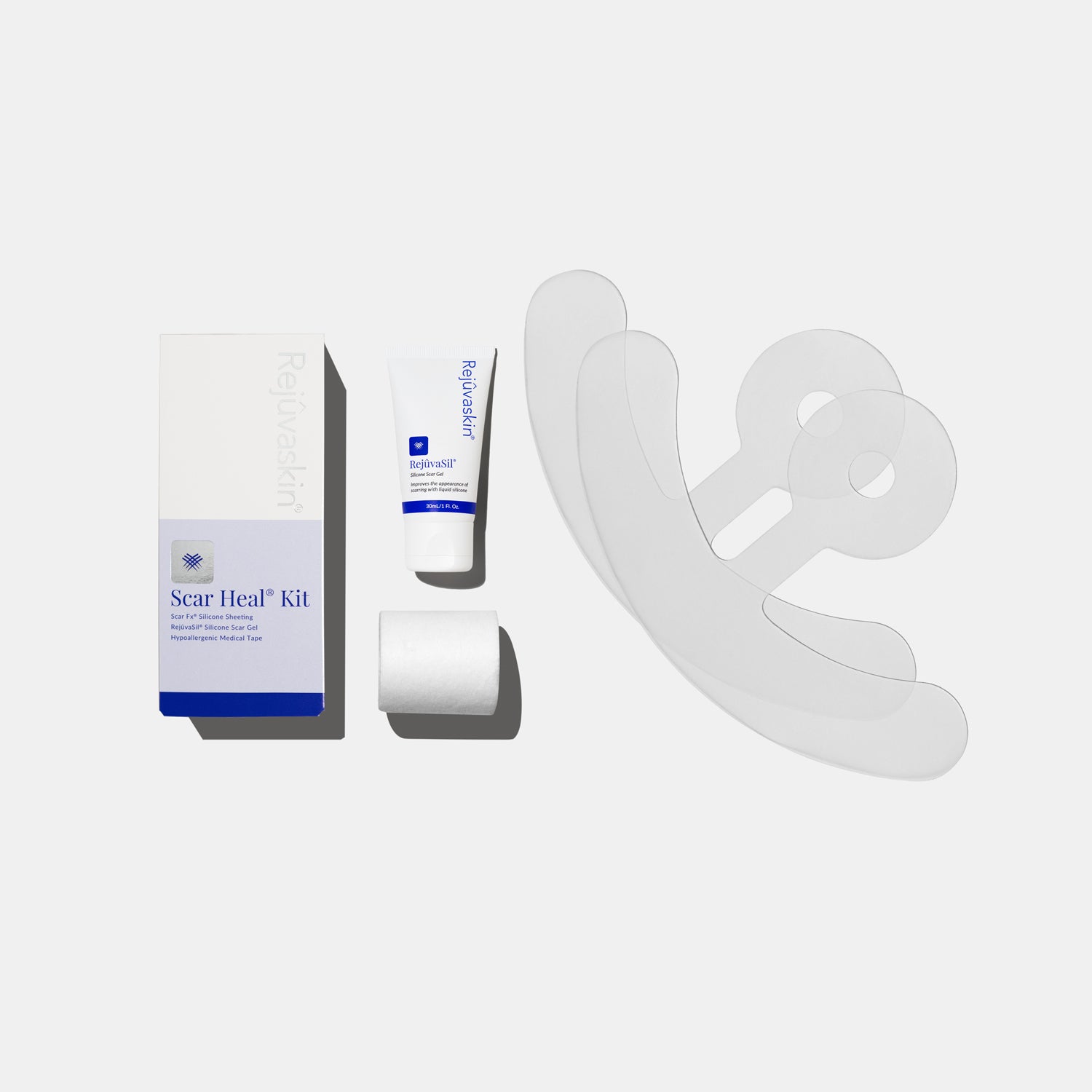
Once your surgeon confirms that your eyelid incisions have fully epithelialized (meaning the wound has closed and is no longer open), using a medical-grade silicone scar gel may help improve the appearance and feel of the surgical scars over time.
Rejuvaskin Rejuvasil Silicone Scar Gel is formulated to create a flexible, breathable silicone layer over healed skin that supports hydration and may help guide the remodeling phase of scar tissue. The scientific literature supports silicone gel as a first-line modality for post-surgical scarring, particularly when used consistently for clinically recommended durations (often several months). (Wang et al., 2020)
Rejuvasil’s ease of use and silicone-based formulation align with evidence from scar management research showing that silicone gels can support outcomes such as reduced scar thickness and improved pliability when compared to untreated scars. (Wang et al., 2020)
Practical Aftercare Considerations
After blepharoplasty, surgeons typically recommend:
-
Protecting the healing incision from excessive tension or friction
-
Minimizing sun exposure and using surgeon-approved sun protection once appropriate
-
Avoiding harsh exfoliants or cosmetic irritants near the eyelid area until healing is established
Using a silicone scar gel like Rejuvasil — after the incision has completely closed and with your surgeon’s guidance — fits within evidence-based scar management practices for patients focused on aesthetic outcomes.
The growth in blepharoplasty demand among women in their 30s reflects evolving aesthetic goals, earlier intervention for both hereditary and aging signs, and broader acceptance of cosmetic surgery. Peer-reviewed clinical literature supports blepharoplasty’s safety and effectiveness when performed by experienced surgeons, and scar management research corroborates the role of silicone gel in supporting optimal scar maturation after surgical healing.
For patients considering an eyelid lift, understanding both the surgical science and post-operative care options, including evidence-supported scar products, is crucial for confident decision-making and long-term satisfaction.
Works Cited
Naik, M. N., Mysore, E., & Ramdial, P. K. (2009). Blepharoplasty: An overview. Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery, PMC2840922. Retrieved from link
Oestreicher, J., McLellan, B., & Carpenter, R. (2012). Complications of blepharoplasty: Prevention and management. Facial Plastic Surgery Clinics of North America, PMC3357590. Retrieved from link
Wang, F., Li, X., Wang, X., Jiang, X., et al. (2020). Efficacy of topical silicone gel in scar management: A systematic review and meta-analysis. International Wound Journal. Retrieved from link
Kim, S. M., Oh, H., Won, C.-H., et al. (2014). Prevention of postsurgical scars: Comparison of silicone gel and silicone gel sheet efficacy. Journal of Korean Medical Science, 29(S3), S249-S254. Retrieved from link
Tandara, A. A., & Mustoe, T. A. (2008). The mechanism of action of silicone gel sheeting in scar management. Aesthetic Plastic Surgery. Retrieved from link



















Leave a comment