We won’t sugarcoat it: getting a breast cancer diagnosis can be scary. A single appointment can turn your world upside-down. One thing that can ease the anxiety, however, is being prepared for what comes next. There are a variety of breast cancer treatments, including radiation therapy, chemotherapy, and surgery.
If your doctor has opted surgery as the best course of action to root out the cancer, you will be weighing 2 options: a mastectomy vs lumpectomy. But what’s the difference between these procedures? Here’s what to expect.
What Is A Mastectomy?
A mastectomy is a surgical procedure that involves removing the entire breast. There are actually six different types of mastectomy:
| Total (Simple) Mastectomy | Involves the removal of the entire breast, including the nipple, areola, and breast tissue, but not the lymph nodes under the arm or muscles beneath the breast. |
| Modified Radical Mastectomy | This procedure removes the entire breast along with some of the lymph nodes under the arm (axillary lymph nodes). It is often used when the cancer has spread to nearby lymph nodes. |
| Radical Mastectomy | The most extensive type, this involves removing the breast, axillary lymph nodes, and the chest wall muscles under the breast. It is less commonly performed today, as other less invasive procedures can be as effective for most patients. |
| Skin-Sparing Mastectomy | Most of the breast tissue is removed, but the skin of the breast is preserved. This is often done when immediate breast reconstruction is planned. |
| Nipple-Sparing Mastectomy | The breast tissue is removed while preserving the skin, nipple, and areola. This is typically an option for women whose tumors are not close to the nipple area. |
| Double (Bilateral) Mastectomy | This refers to the removal of both breasts, often performed as a preventive measure in women at high risk for breast cancer, such as those with BRCA gene mutations. |
Mastectomies are typically recommended for patients with more advanced breast cancers or those who have tumors close to their chest wall; it may also be advised if radiation therapy isn't an option.
What Is A Lumpectomy?
Full breast-removing mastectomies can be quite a life-altering procedure. Luckily, they’re not always needed. A lumpectomy is a breast-conserving procedure in which breast tissue and some of the underlying breast glandular tissue are removed. The nipple, areola, and breast skin remain intact.
Lumpectomies may be performed if there's no evidence that cancer has spread to the surrounding breast tissue or lymph nodes since it removes only the tumor without removing any breast tissue. It is generally used as the first line of defense against less aggressive tumors in the early stages of development.
What Preparation and Aftercare Is Like: Mastectomy vs. Lumpectomy
Mastectomy Prep
Before heading into the hospital for surgery, there are a few things you’ll want to do before your mastectomy. These can include:
- Cease breastfeeding
- Inform your doctor about any medications, vitamins, or supplements you take
- Refrain from sexual activity
- Wear loose, comfy clothes
- Stop taking aspirin or other blood-thinning medications
- Don’t eat or drink anything for 8-12 hours before the procedure
After the surgery has concluded, you will likely spend the night in the hospital, where your doctor will give you specific aftercare instructions. Typically, it is recommended that you wear compression garments for a few weeks after surgery to prevent swelling, and that you use arm crutches to help you stand and walk. For those considering breast reconstruction afterwards, you’ll also want to start talking to your doctor about the best implant options for you.
Lumpectomy Prep
Much of the prep and aftercare for a lumpectomy is very similar to a mastectomy, depending on the severity of the procedure. The main difference, however, is that lumpectomy surgery is usually an outpatient procedure with the patient returning home on the same day and can return to work within two or three days following their operation. Your mobility will also likely be limited for a few weeks after the procedure, so make sure to have those crutches on hand.
What Kind of Scarring Results From A Mastectomy vs. Lumpectomy
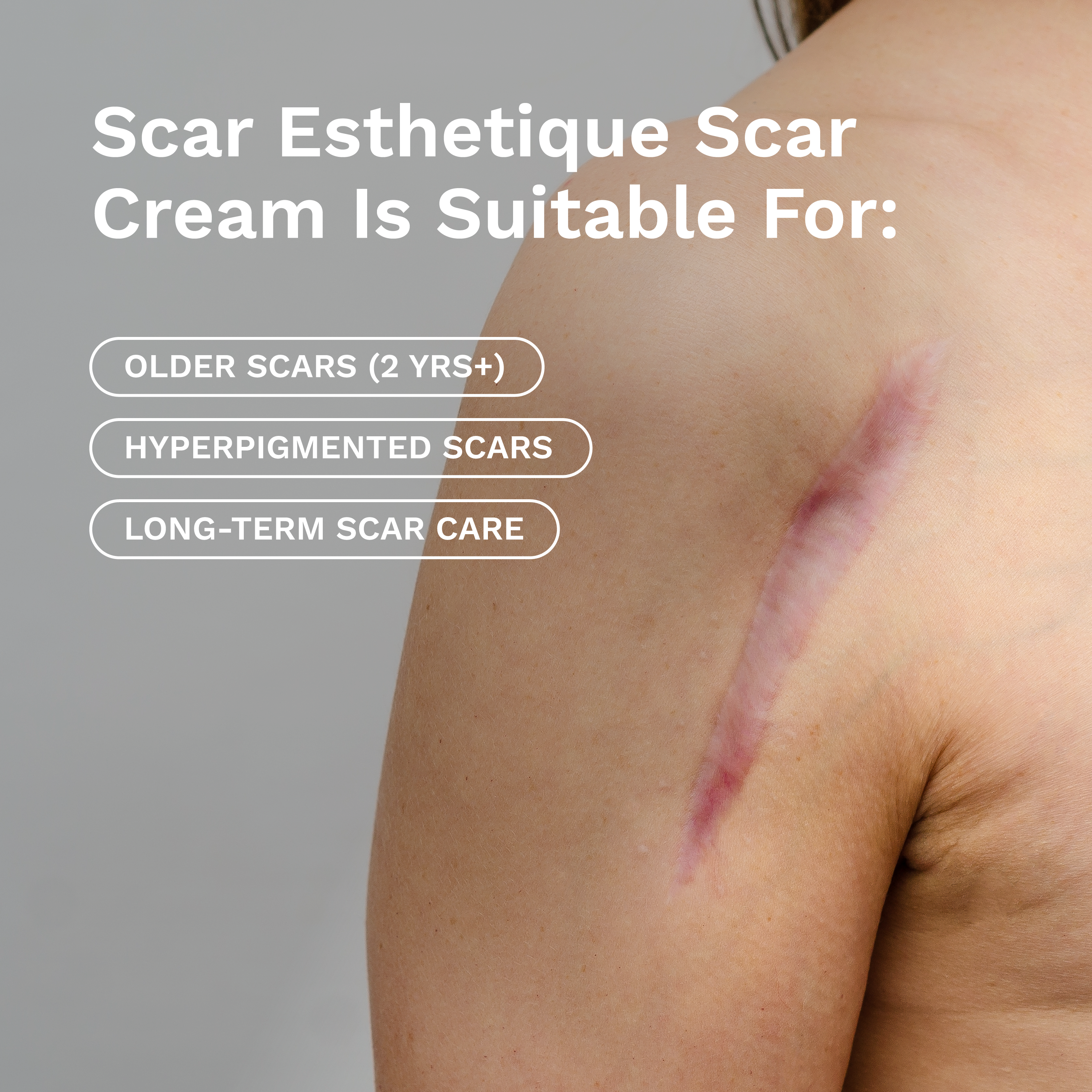
Mastectomy Scars
During a mastectomy, a surgeon removes tissue from one or both breasts, taking out either a portion or the entire breast. A surgeon's incision location and type determine the type and location of scarring afterwards. Nevertheless, a mastectomy usually leaves a large scar on either side of the breastbone.
Lumpectomy Scars
A lumpectomy leaves a smaller scar on the breastbone; depending on where surgery was performed, these scars may also be hidden in the crease beneath the breast or around the nipple.
Take Care of Your Breast Procedure Scars
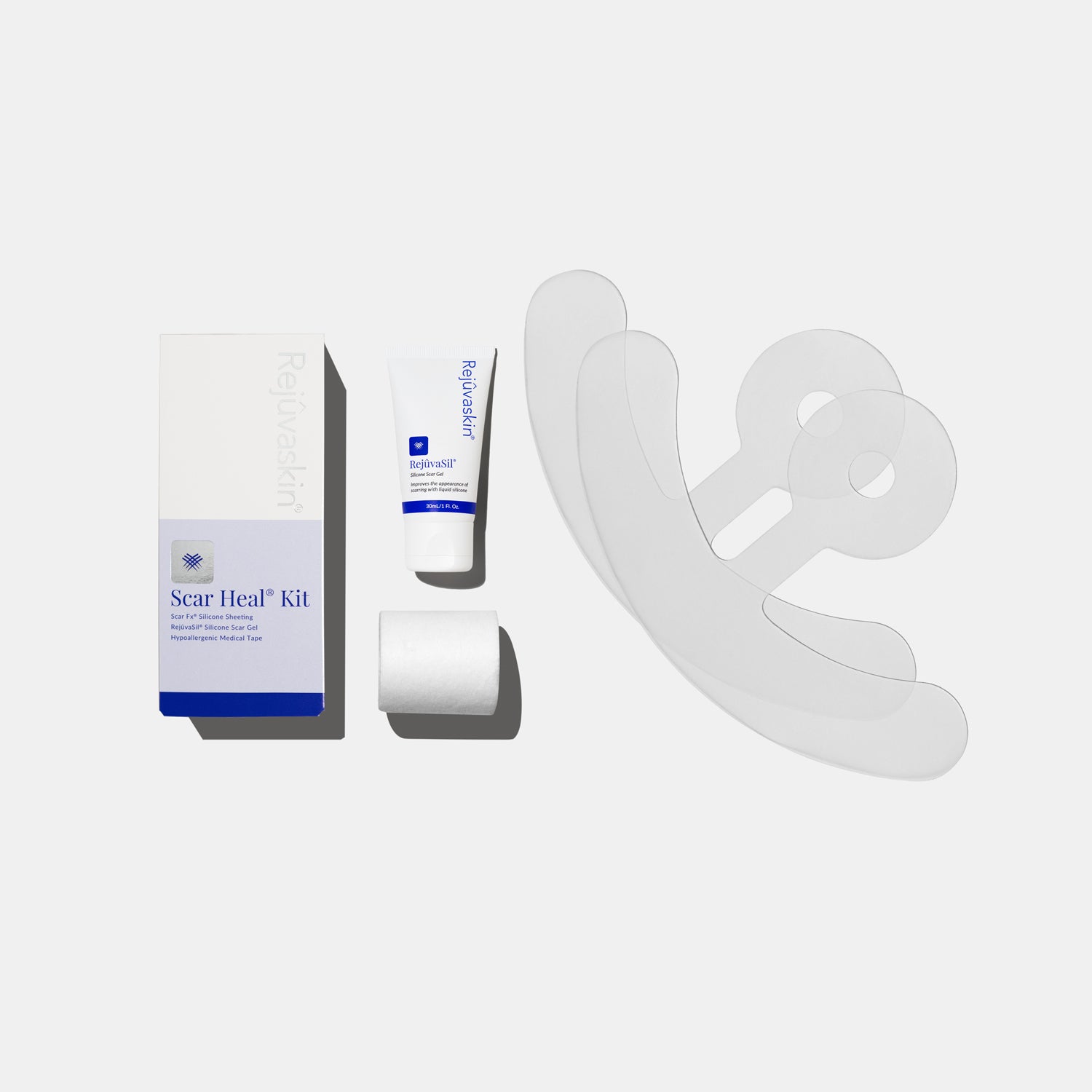
While both of these procedures will produce scars, it's essential to prepare and care for your scar to minimize its appearance with scar management products, such as Rejuvaskin. While the internet is full of tips, tricks, and products that promise to heal scars, we can tell you that silicone is by far the best scar-healing ingredient. Check out Rejuvaskin's Scar Fx silicone sheeting, recommended by plastic surgeons and dermatologists worldwide.



















Leave a comment