Experiencing eczema flare-ups or post-radiation skin irritation? You’re not alone—and your skin’s microbiome could be the key to faster recovery. Discover how powerful plant-based ingredients like calendula, aloe, hyaluronic acid, and pea extract can soothe, hydrate, and help restore your skin’s natural microbial balance.
1. Why a Balanced Microbiome Matters
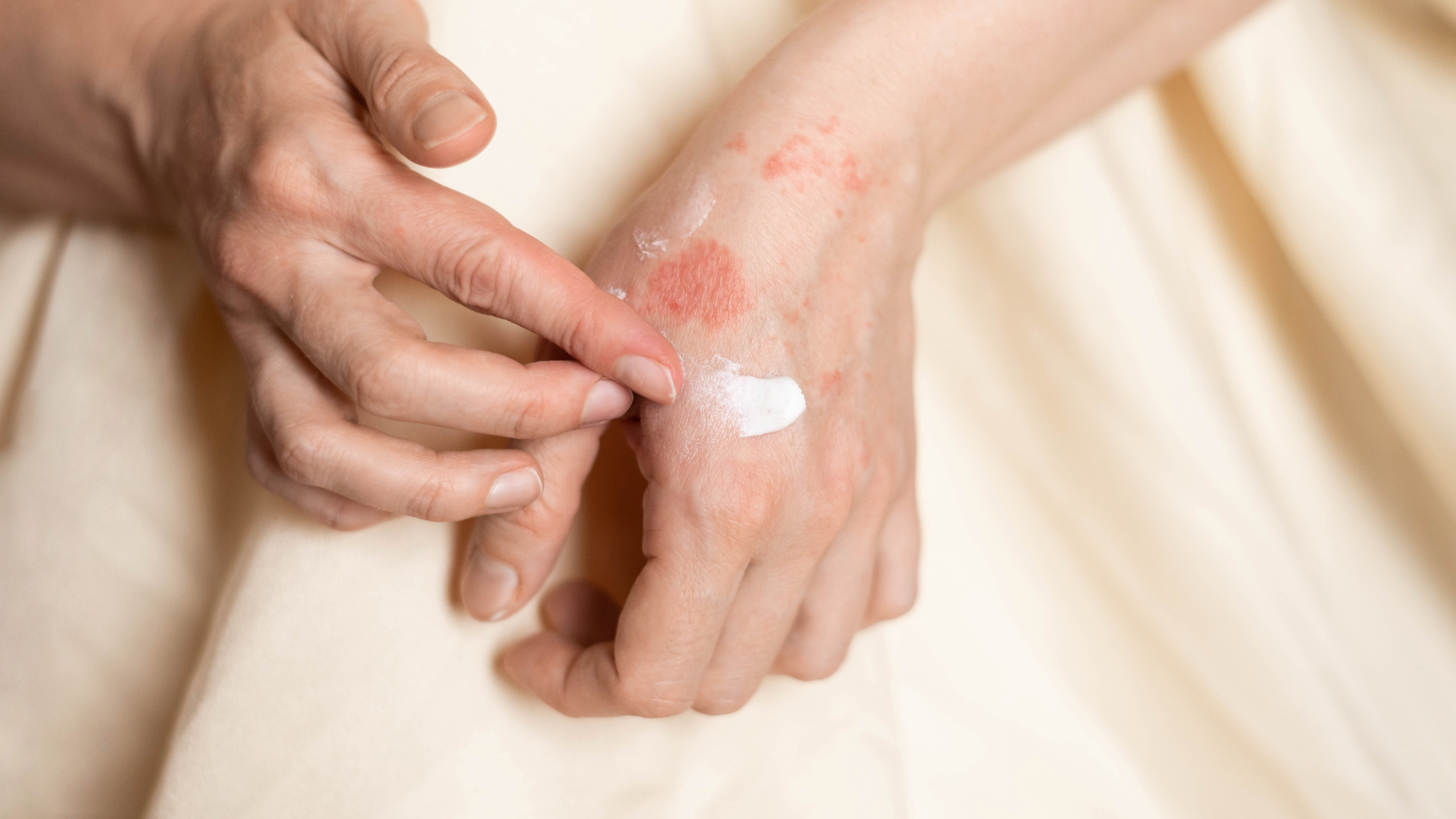
After eczema or radiation therapy, the skin’s delicate ecosystem of bacteria—its microbiome—often falls out of balance. This can lead to inflammation, sensitivity, and slow healing. Studies show that a disrupted microbiome contributes to both the severity and recurrence of eczema symptoms and radiation-induced dermatitis (Hülpüsch et al., 2024).
2. Botanical Heroes with Scientific Backing
Calendula
This golden flower does more than look pretty. Calendula is packed with flavonoids that calm inflammation and support a microbiome-friendly environment, making it ideal for sensitive or damaged skin.
Aloe Vera
Aloe isn’t just soothing—it’s also antimicrobial and hydrating. By cooling irritated skin and reducing inflammation, aloe helps beneficial bacteria thrive again.
Hyaluronic Acid (HA)
This moisture magnet helps repair a weakened skin barrier—an essential step to rebuild a healthy microbial ecosystem. Research shows that skin hydration supports microbiome restoration.
Pea Extract
Rich in plant peptides and prebiotics, pea extract may help stimulate skin renewal and nourish healthy microbial growth—particularly important after irritation or damage.
3. What the Research Says
-
Radiation Recovery: Topical sucralfate cream significantly reduced skin reactions and improved healing time in breast cancer patients undergoing radiation, reinforcing the importance of barrier repair (Maiche et al., 1994).
-
Eczema Support: A lipid-rich foam cream restored the skin barrier far more effectively than basic creams in patients with mild atopic eczema.
-
Microbiome-Based Skincare: Probiotics and postbiotics show promise for balancing the skin microbiome, improving barrier function, and reducing inflammation in eczema-prone and post-treatment skin (De Almeida et al., 2023), (Tavaria, 2017).
4. Rejuvaskin's Skin Recovery Cream: A Clean-Botanical Blend
At Rejûvaskin, we understand how vulnerable your skin can feel after harsh treatments. That’s why our Skin Recovery Cream includes gentle yet effective botanicals designed to nourish and protect:
Calendula & Aloe – Calm irritation and reduce redness
Hyaluronic Acid – Deeply hydrates and restores flexibility
Pea Extract – Helps feed and stabilize the skin’s microbiome
Fragrance-Free & Dermatologist-Approved – Safe for the most sensitive skin
The formula is lightweight yet powerful—perfect for skin recovering from eczema, barrier disruption, or cosmetic treatments.
5. Daily Tips for Microbiome Recovery
|
Do This |
Why It Helps |
|
Choose barrier-repair creams |
Support beneficial microbes and reduce inflammation |
|
Avoid harsh exfoliants or acids |
These strip away protective bacteria |
|
Stay hydrated |
Hydration enhances microbiome balance |
|
Simplify your skincare routine |
Too many actives can throw off your flora |
|
Avoid fragrance and alcohol |
These irritants can kill healthy bacteria |
Your microbiome is your skin’s first defense. And after eczema or radiation therapy, giving it the right tools to recover is key. Gentle botanicals like calendula, aloe, hyaluronic acid, and pea extract offer natural, science-backed solutions that help soothe and strengthen the skin from the inside out.
For everyday use or as part of your post-treatment recovery plan, Rejûvaskin’s Skin Recovery Cream is microbiome-friendly care you can trust.
Works Cited
-
De Almeida, C. V., Antiga, E., & Lulli, M. (2023). Oral and Topical Probiotics and Postbiotics in Skincare and Dermatological Therapy. Microorganisms, 11.
-
Dähnhardt, D., Dähnhardt-Pfeiffer, S., Schulte-Walter, J., et al. (2022). Comparison of Lipid Foam Cream and Basic Cream on Epidermal Reconstruction in Mild Atopic Eczema. Skin Pharmacology and Physiology, 35, 282–290.
-
Hülpüsch, C., Rohayem, R., Reiger, M., & Traidl-Hoffmann, C. (2024). Exploring the Skin Microbiome in Atopic Dermatitis Pathogenesis and Disease Modification. Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology.
-
Maiche, A., Isokangas, O., & Gröhn, P. (1994). Skin Protection by Sucralfate Cream During Electron Beam Therapy. Acta Oncologica, 33(2), 201–203.
-
Richardson, B. N., Lin, J. Y., Buchwald, Z., & Bai, J. (2022). Skin Microbiome and Treatment-Related Skin Toxicities in Patients with Cancer. Frontiers in Oncology, 12.
-
Tavaria, J. (2017). Topical Use of Probiotics: The Natural Balance. Porto Biomedical Journal, 2(3), 69–70.



















Leave a comment